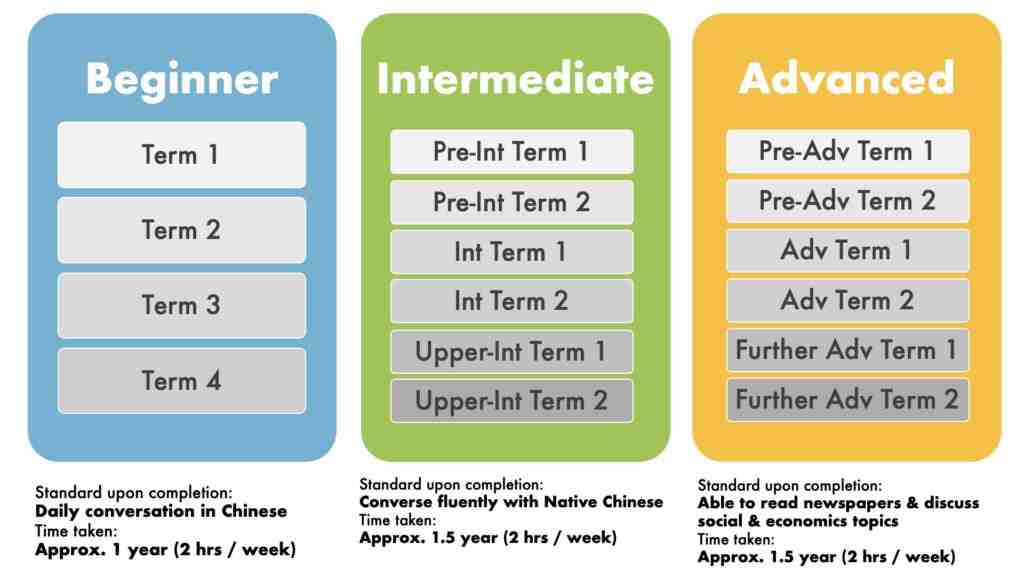
The decision between Business Chinese and Conversational Chinese depends on individual goals, interests, and practical needs. For professionals aiming to excel in international business environments or seeking career opportunities in China or other Chinese-speaking regions, prioritizing Business Chinese is advisable. Conversely, individuals prioritizing personal enrichment, cultural immersion, or travel may find Conversational Chinese more suitable, as it equips them with the language skills necessary for everyday interactions and cultural experiences.