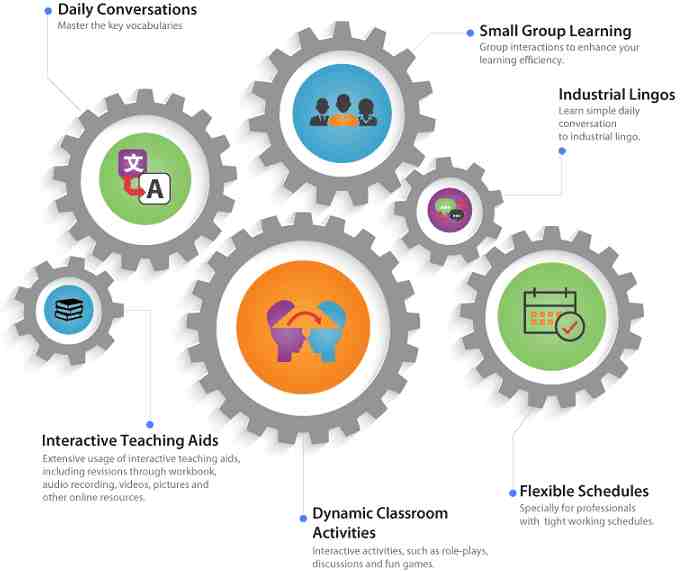
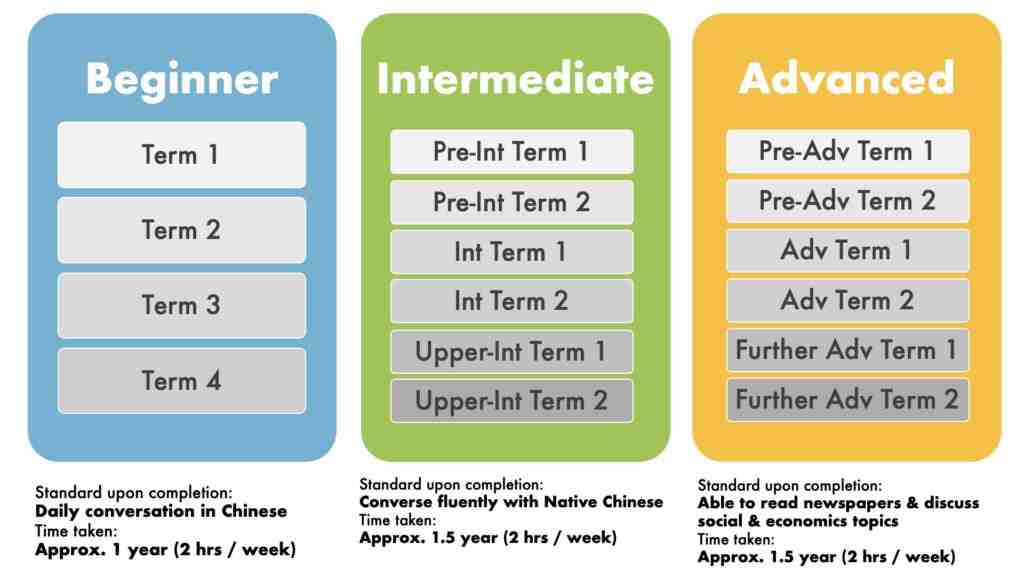
How to Write a Professional Email in Mandarin
How to Write a Professional Email in Mandarin
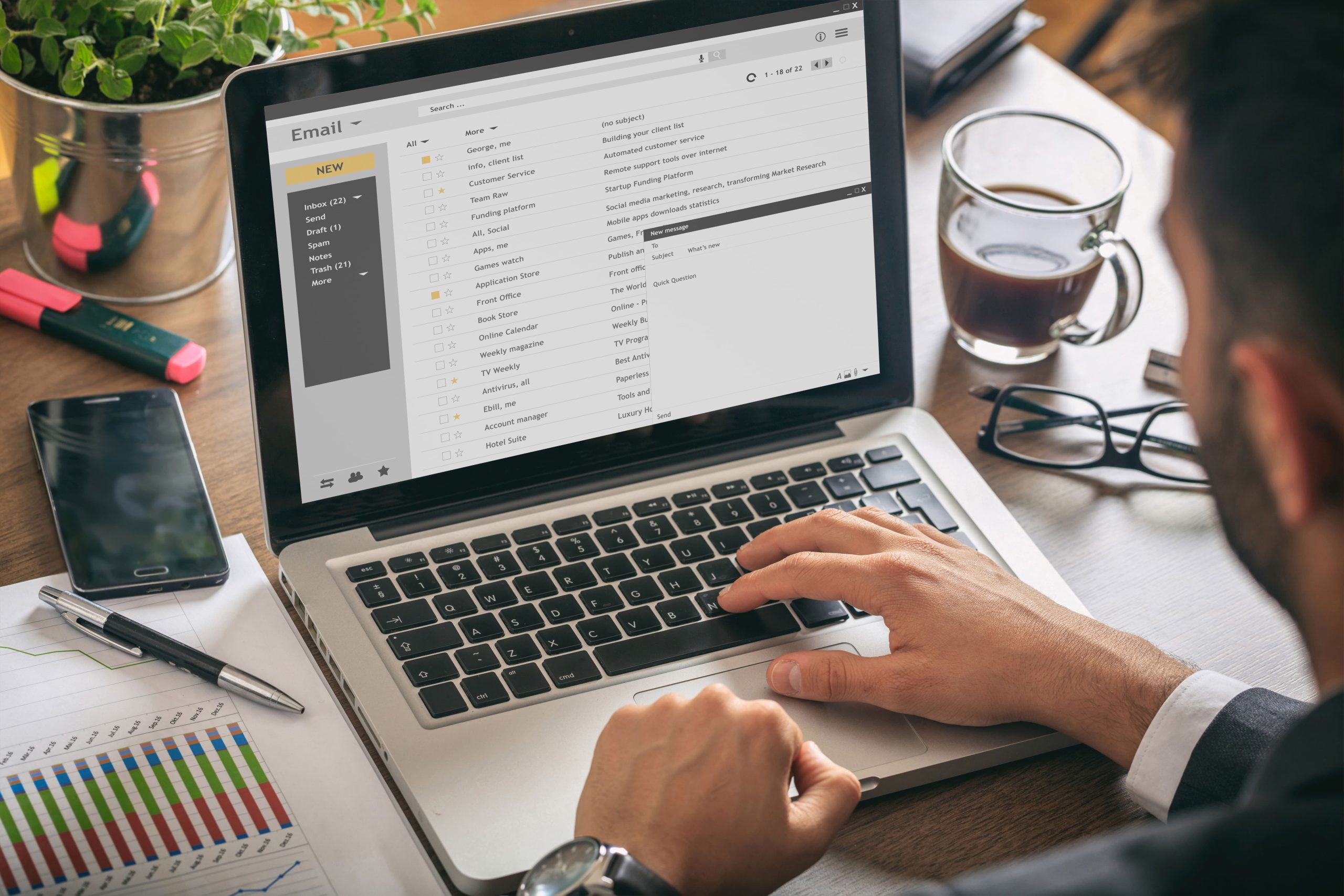

Communicating can come in many different forms and is not limited to verbal communication. In business settings, communicating through written media, such as emails and text is commonly used. A study on the average daily worker shows that a typical employee will receive approximately 40 emails a day. This number shows the importance of email for communication.
As mentioned previously, Mandarin is widely utilized in professional environments, establishing itself as a standard language for various business interactions. This existence remains the same for written communication, exhibiting how fluency in Mandarin is equally important for written media. This means, you need to learn how to write a professional email in Mandarin especially in business settings. In the following section, we will be discussing how to write professional emails in Mandarin and standardized etiquette when sending them.

The Structure of a Professional Mandarin Email : Essential Parts When Writing Professional Emails in Mandarin
To start writing a professional email in Mandarin, it is essential to start with familiarizing yourself with the structure. Learning the right structure will assist you in composing a clear and concise message that can be understood by other parties easily. Typically, emails are formed with the following structure
- Email subject
Email subject is usually written along with the recipient of the email. This part is usually utilized to give a brief overview of what you are writing about. Email subject is commonly constructed in short sentences, consisting only 6-10 words to serve its purpose as a short summary of the message’s intention. For instance, you can write 会议安排 if you are writing about business meetings to other parties. - Title and Greetings
Being able to engage actively with others while communicating is utmost important. When writing an email to someone, make sure to address them beforehand to acknowledge the person you are writing to. Generally, there are two situations when addressing people. If you happen to know the specific person you are writing to, it is highly recommended to put their title or position in the first line. However, if the email is not targeted to a specific person, you can try using ___ 的相关负责人 which means ___’s related staff and can be utilized similar to “to whom it may concern”
After writing a proper title to address the recipient, you can easily add a greeting such as 您好 before jumping into the body email. - Body Contents
Body contents are the most important part of professional email as it will be showing the message that you intend to share with the recipient. While being respectful is important, try keeping the message short and concise, especially with how many emails someone might read in a day. - Closing
After the body contents have been delivered to the recipient, another part to pay attention to is how you sign off from the email. The standard phrase that is commonly applied to close an email is 此致敬礼 which can be translated into “best regards” - Signature and Attachment
Signing off with a signature is highly recommended, especially if you’re sending a professional email. Writing a signature that consists of basic information such as your name and your company’s contact information will help ensure your credibility. Furthermore, if you have any attachments that need to be sent together, make sure to mention about its existence on the body contents.

Know the Phrases: Common Mandarin Terms for Professional Emails
As China has shown its strong presence in the global economy, writing in Mandarin may become inevitable. That’s why developing skills in writing a professional email in Mandarin is necessary on everyday’s business interactions. As a basic guideline, here’s a few common Mandarin terms that you will most likely use while composing written media.
- 感谢您抽出时间与我联系
Gǎnxiè nín chōuchū shíjiān yǔ wǒ liánxì
“Thank you for taking your time to contact us”
- 如有不便之处,敬请见谅
Ru yǒu bú biàn zhī chù, jìng qǐng jiàn liàng
“We apologise for any kind of inconvenience”
- 很抱歉没有及时回复
Hěn bào qiàn méi yǒu jí shí huí fù
“I apologise for the late reply”
- 希望您能考虑
Xīwàng nín néng kǎolǜ
“I hope you can consider it.”
- 附件是___,请查收
Fù jiàn shì ____ qǐng chá shōu
“Please find the attached ____ here”
- 我们很期待跟贵公司的合作
Wǒ men hěn qī dài gēn guì gōng sī de hé zuò
“We are looking forward to working with your company”
Master the Etiquette: Different Things to Pay Attention to
After knowing the structure and phrases to start with, paying attention to etiquette is equally important, especially in business settings. Since you will be sending emails that represent your professionalism and possibly your organization, adhering to proper etiquette can help you avoid misunderstandings and maintain respect. Here’s a few basic etiquette to implement while interacting with business professionals
-
- Provide enough context/background – While writing a professional email in Mandarin, make sure to leave enough context for the recipient, especially if you’re writing for collaboration or seeking for assistance. Providing context will help recipients to be able to make a decision based on the real situation happening around them.
- Write concisely – As previously mentioned, an average worker will receive an abundance of emails to be reviewed. Therefore, it is recommended to keep the message short without shifting its meaning.
- Organize information – Professional emails in Mandarin demand the sender to be able to organize a good flow of information without oversharing any unnecessary details. While crafting a professional email, it is advised to use the inverted pyramid method, in which the most important information will be dominating the body contents and is best to be delivered first.
- Be respectful – Professional emails are meant to be sent on formal settings, such as business occasions. Therefore, you should treat professional emails carefully, writing in a respectful tone. Avoid using slang and abbreviations since it can cause misunderstanding in the future.